U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency’s new Malware Analysis Report on a malicious listener deployed on Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM) systems by chaining CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428 during real-world intrusions. The report ships with indicators of compromise, YARA and SIGMA rules, and clear mitigation guidance, making it a must-read for defenders managing mobile device fleets and MDM infrastructure.
What happened
CISA analyzed two sets of malware recovered from an organization where threat actors exploited Ivanti EPMM vulnerabilities CVE-2025-4427 (authentication bypass) and CVE-2025-4428 (remote code execution), ultimately installing a malicious listener to run arbitrary code on the server. The agency’s advisory and technical report detail how the chain was used after public proof-of-concept code appeared, and they provide concrete detection content and response steps.
Why it matters
EPMM is core mobile device management infrastructure; compromise at this tier can cascade into control over large fleets of managed devices and enterprise identity stores, elevating risk far beyond a single server breach. CISA added both flaws to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog in May, underscoring the urgency of patching and hardening exposed EPMM instances.
How the attack works
According to CISA’s technical analysis, actors first abused CVE-2025-4427 to reach an internal API endpoint at /mifs/rs/api/v2 via crafted HTTP GET requests, misusing the ?format= parameter to advance the intrusion. They then leveraged server-side template injection to trigger CVE-2025-4428 and achieve remote code execution, enabling a series of follow-on commands.
Visual: Flowchart of the exploit chain showing how CVE-2025-4427 enables access to the API, which is then paired with CVE-2025-4428 to run commands, harvest credentials, and deploy a persistent malicious listener, as documented in CISA AR25-261A.
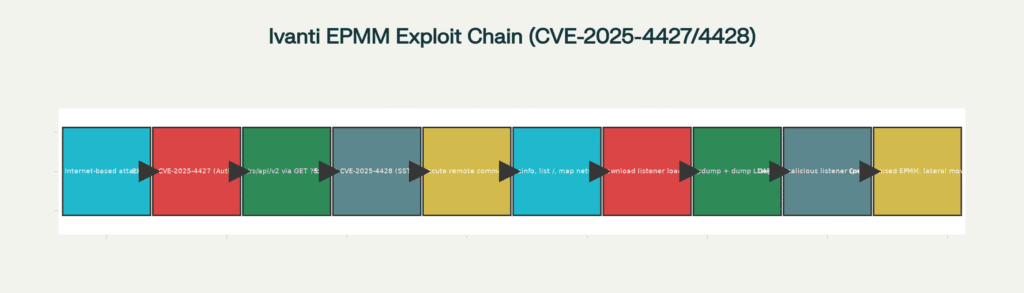
Exploit chain used to deploy a malicious listener on Ivanti EPMM as documented by CISA MAR AR25-261A
What attackers did post-exploit
Once code execution was established, the operators executed commands to collect system information, list the root directory, map the network, and download additional malicious files that act as “listener loaders” on the server. They also created a heapdump and dumped LDAP credentials, then deployed the malicious listener to persist and facilitate arbitrary command execution.
Who is affected
CISA lists affected EPMM versions as 11.12.0.4 and prior, 12.3.0.1 and prior, 12.4.0.1 and prior, and 12.5.0.0 and prior, with patches made available by Ivanti on May 13, 2025. Ivanti’s advisory confirms updates are available and urges customers to upgrade immediately to supported fixed versions.
CVE quick comparison
| CVE | Type | CVSS (v3) | Summary | Auth required | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-4427 | Auth bypass in EPMM API | 5.3 | Allows access to protected API resources without normal authentication controls in affected versions . | No | NVD details and vendor context confirm bypass of API protections . |
| CVE-2025-4428 | Remote code execution in EPMM API | 7.2 | Enables command execution on vulnerable systems when reached via the API in affected versions . | Yes (but chained for unauth RCE) | Chaining with CVE-2025-4427 leads to unauthenticated RCE in practice per multiple analyses . |
Indicators and detection
CISA’s report provides downloadable indicators of compromise tied to the malware, plus YARA and SIGMA rules that teams can operationalize across SOC pipelines and EDR/SIEM to detect the malicious listener and its loaders. The analysis also describes the specific endpoint path, request method, and parameter misuse seen in the attacks, which can inform high-fidelity detections and reverse-proxy/WAF signatures.
Immediate actions for defenders
Upgrade EPMM to the latest fixed versions as directed by Ivanti and validate that vulnerable versions are fully removed from service, not merely firewalled. Import and deploy the YARA and SIGMA rules from CISA, sweep for the published IoCs, and review web/proxy logs for suspicious GET requests to /mifs/rs/api/v2 with anomalous ?format= values.
- Restrict direct access to EPMM APIs using portal ACLs and/or an external WAF, as this materially reduces exposure to the initial access vector described in the exploit chain.
- Treat MDM systems as high-value assets by tightening monitoring, restricting administrative access, and segmenting them from general user networks in line with CISA’s guidance.
- If indicators are present, assume credential exposure; rotate LDAP service credentials and investigate potential lateral movement from the EPMM host.
Primary sources to bookmark
CISA’s alert announces the release and highlights the availability of malware indicators and detection rules for defenders. The full Malware Analysis Report AR25-261A contains the technical deep-dive on exploitation flow, observed commands, IoCs, and defensive content, including confirmation of KEV status for the CVEs. Ivanti’s advisory provides patch availability and upgrade guidance that should be actioned without delay.
What happened
- https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/alerts/2025/09/18/cisa-releases-malware-analysis-report-malicious-listener-targeting-ivanti-endpoint-manager-mobile
- https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/analysis-reports/ar25-261a
- https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/Security-Advisory-Ivanti-Endpoint-Manager-Mobile-EPMM
- https://www.tenable.com/blog/cve-2025-4427-cve-2025-4428-ivanti-endpoint-manager-mobile-epmm-remote-code-execution